How to Calculate Productivity: A Comprehensive Guide

Calculating productivity is key to ensuring a business operates efficiently, effectively utilizing resources to produce the maximum output possible. Whether it’s tracking employee performance, resource utilization, or overall company performance, understanding productivity can lead to significant gains. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the concept of productivity in business, its importance, and several formulas and methods to calculate it accurately.
What is productivity in business?
In a business context, productivity refers to the measure of efficiency with which inputs—such as labor, capital, and materials—are transformed into outputs, like goods or services.
At its core, productivity is about maximizing output while minimizing the use of resources. For example, a company that manufactures cars is considered more productive if it can produce more vehicles using the same or fewer inputs (e.g., labor, materials, and time) than its competitors. Similarly, a sales team’s productivity might be evaluated by how many sales they close within a certain period, given the number of hours worked.
The concept of productivity is critical in every business sector, whether it’s a manufacturing company, a service provider, or even a creative agency. High productivity often leads to increased profitability, better customer satisfaction, and more efficient use of resources, all of which contribute to long-term growth and sustainability.

Why Calculate Productivity?
Calculating productivity allows businesses to monitor performance, identify bottlenecks, and optimize operations.
Here are some key reasons why calculating productivity is essential:
Identifying Inefficiencies: By calculating productivity, companies can spot areas where resources are being underutilized or wasted. For instance, if a team is consistently falling behind on deadlines, the data could reveal that time is being lost to inefficient processes or poor task management.
Performance Monitoring: Productivity metrics enable businesses to track both individual and team performance over time. Regular monitoring ensures that employees remain productive and focused on their key tasks.
Improving Profit Margins: Higher productivity often leads to greater output with the same or fewer inputs, which helps businesses boost profit margins. This is particularly important in industries with high competition, where small gains in productivity can lead to significant financial advantages.
Resource Allocation: Productivity data helps managers allocate resources more effectively. By understanding where productivity is highest, businesses can ensure that labor, capital, and materials are directed toward high-impact areas.
Employee Engagement: When employees see their work contributing to measurable productivity goals, they often feel more engaged and motivated. Productivity metrics can be used to set clear performance expectations and reward those who excel.
What Is the Productivity Formula?
The most common productivity formula is:
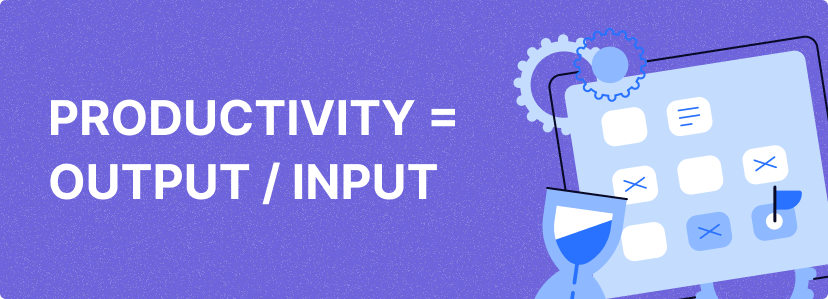
Productivity = Output / Input
This basic formula provides a general sense of how efficiently a business is operating. Output could be anything from the number of products made to services delivered, while input could include resources such as labor, materials, or capital. This formula can be adapted depending on the specific type of productivity being measured. For example, if you’re calculating labor productivity, the output would be the total goods or services produced, and the input would be labor hours. Example: If a company produces 10,000 units of a product using 2,000 hours of labor, the productivity would be:
Productivity = 10,000 units / 2,000 hours = 5 units per hour
Labor Productivity Formula
Labor productivity is a key metric used to measure the efficiency of labor inputs in the production process.

It’s calculated as: Labor Productivity = Total Output / Total Labor Hours
This formula is particularly useful for businesses where human labor is the primary input, such as in manufacturing or services. By monitoring labor productivity, companies can assess how effectively their workforce is being utilized.
Example: A software development firm may complete 20 software projects over a quarter, using 10,000 hours of labor. The labor productivity would be:
Labor Productivity = 20 projects / 10,000 hours = 0.002 projects per hour
Multifactor Productivity
Multifactor productivity (MFP) provides a more comprehensive view by taking into account multiple inputs—such as labor, capital, and materials—into a single efficiency metric.

It’s calculated as: Multifactor Productivity = Total Output / (Labor + Capital + Materials)
Multifactor productivity is particularly useful in industries that rely on multiple resources to produce output, like manufacturing or construction. This metric provides a broader understanding of the efficiency of an entire production process, not just one input.
Partial Factor Productivity
Partial factor productivity focuses on one specific input, such as labor, capital, or energy, to measure productivity. The most commonly used partial factor productivity measure is labor productivity, but capital and energy productivity are also important.

For example, capital productivity can be calculated as:
Capital Productivity = Output / Capital Input
Partial factor productivity allows companies to isolate and measure the efficiency of a single resource. Example: A factory may produce 50,000 widgets using $100,000 worth of raw materials. The material productivity would be: Material Productivity = 50,000 units / $100,000 = 0.5 units per dollar
Productivity Metrics
Productivity metrics are used to measure efficiency at both the employee and organizational levels. These metrics help businesses track performance and identify areas for improvement.
Revenue per Employee
Revenue per employee is a popular productivity metric, particularly in service-based industries. It measures how much revenue each employee generates and is calculated as:
Revenue per Employee = Total Revenue / Number of Employees
This metric provides insight into how effectively your workforce is contributing to the company’s bottom line.
Example: If a company has $1 million in revenue and 50 employees, the revenue per employee would be:
Revenue per Employee = $1 million / 50 employees = $20,000 per employee
Personal Feedback
While quantitative metrics like revenue per employee are valuable, personal feedback from employees is another important indicator of productivity. Gathering regular feedback can help identify obstacles to productivity, such as unclear goals, insufficient training, or poor task management. By using surveys, one-on-one meetings, or employee feedback platforms, managers can collect qualitative data that informs decision-making and improves team efficiency.
Focus Work and Meeting Rate
Another key productivity metric is the focus work and meeting rate—the ratio of time spent on focused, productive work versus time spent in meetings. This metric helps businesses ensure that employees are spending most of their time on meaningful, high-value tasks rather than being bogged down in unnecessary meetings.
Example: An employee who spends 70% of their day on focused work and 30% in meetings is likely to be more productive than someone who spends 50% or more of their time in meetings. By analyzing these ratios, managers can restructure schedules to maximize focus time and minimize meetings that detract from productivity.
What Are The Top 6 Methods for Calculating Productivity?
There are various methods to calculate productivity depending on the nature of the work and the goals of the business. Here are the top six methods:
1. Relying on the Standard Productivity Formula
The most basic method of calculating productivity is the standard formula: Productivity = Output / Input This formula can be applied universally across industries and provides a general idea of how well resources are being utilized. It’s especially useful for calculating labor productivity or measuring the efficiency of specific business processes.
2. Using the Total Sales Method
Another approach is to calculate productivity based on total sales. This is particularly useful in sales-driven industries, where revenue generation is the primary goal. The formula is: Productivity = Total Sales / Resources Used This method provides insight into how well sales teams or retail operations are performing in terms of converting input resources (e.g., marketing spend, labor, and time) into actual sales.
3. Calculating Revenue per Employee
Revenue per employee is a simple and effective way to gauge the overall productivity of your workforce. As mentioned earlier, this metric measures how much revenue each employee generates, offering insight into whether staffing levels are appropriate and if employees are contributing to profitability.
4. Looking at Objectives & Goals
Another method of calculating productivity is to evaluate whether employees are meeting their set objectives and goals. This approach is more qualitative and often relies on key performance indicators (KPIs) specific to each role or department. For example, a marketing team might have a goal of generating 100 leads per month. The productivity of the team can be calculated based on whether they consistently meet or exceed this target.
5. Collecting Employee Feedback
Collecting feedback directly from employees can also be a useful method for gauging productivity. By conducting surveys or holding one-on-one meetings, managers can gather insights into roadblocks that might be hindering productivity. These insights can be used to improve workflows, adjust goals, and create a more productive work environment.
6. Productivity Tracking Software
One of the most effective ways to calculate and improve productivity is by using productivity tracking software like Monitask. These tools track the time employees spend on different tasks, measure their focus levels, and provide reports on overall productivity. Software can automatically calculate how much time is being spent on high-priority tasks versus distractions, offering a real-time view of productivity. Monitask also helps track the progress of projects, providing managers with a comprehensive overview of team performance.
Considerations when Calculating Productivity

When calculating productivity, it’s crucial to consider several factors. First, industry type plays a key role, as productivity metrics can vary depending on the field.
In manufacturing, for instance, labor productivity might focus on units produced, while in the service sector, it could be based on customer satisfaction or response times. Second, external factors such as market conditions, competition, and economic trends can also impact productivity.
For example, during an economic downturn, reduced customer demand may affect revenue per employee, even if the team’s performance remains steady. Third, there’s the balance of quality versus quantity.
Focusing solely on output can sometimes cause quality to decline. It’s essential to strike the right balance between high output and maintaining quality standards, particularly in industries where customer satisfaction is vital. Lastly, team dynamics are crucial in productivity. It’s not just about individual performance; collaboration, leadership, and company culture significantly influence productivity. High-performing teams typically have clear goals, effective communication, and a sense of ownership over their work, which boosts overall productivity.
How to Improve Productivity with Monitask Time Tracker?
Monitask is a powerful productivity tracking tool that can help businesses improve productivity in several ways: Real-Time Time Tracking: Monitask enables businesses to track how much time employees spend on various tasks throughout the day. This data helps managers identify inefficiencies, reduce idle time, and ensure that employees are focusing on high-priority tasks.
Detailed Reports: With Monitask, managers can generate detailed productivity reports that offer insights into employee performance, project progress, and overall productivity levels. These reports can be used to make data-driven decisions about resource allocation, task delegation, and team management.
Idle Time Monitoring: Monitask tracks idle time, giving managers a clearer picture of how productive employees are throughout the day. This feature helps identify distractions or unnecessary breaks that might be hindering performance.
Task and Goal Tracking: The platform allows businesses to set clear goals for employees and track their progress over time. Employees can see how their work contributes to larger objectives, helping them stay focused and motivated.
Screenshots and Activity Monitoring: Monitask captures screenshots and tracks activity levels to provide managers with a transparent view of employee productivity. This helps ensure accountability and encourages employees to stay on task.
Boost Employee Accountability: By using Monitask, employees become more aware of how their time is being used. This increased accountability often leads to improved time management and better overall productivity.
Conclusion
Calculating productivity is essential for improving efficiency, performance, and profitability in business. By understanding and applying the right formulas, such as Output/Input or Revenue per Employee, businesses can optimize their operations and make informed decisions.
Various methods—including employee feedback, goal tracking, and productivity software like Monitask—can be used to measure and enhance productivity. Ultimately, productivity isn’t just about getting more done—it’s about working smarter, optimizing resources, and continually improving processes.
By using tools like Monitask, businesses can ensure they are maximizing efficiency, minimizing waste, and achieving long-term success.
FAQ
What is the standard productivity formula?
The standard formula is Productivity = Output / Input. It can be used to measure the efficiency of various inputs like labor, capital, and materials.
How can Monitask improve productivity?
Monitask helps businesses track employee time, monitor activity, reduce idle time, and generate reports to improve overall productivity.
What is revenue per employee?
Revenue per employee is a productivity metric that measures how much revenue each employee generates. It’s calculated as Total Revenue / Number of Employees.
How does feedback influence productivity?
Employee feedback provides insights into roadblocks and inefficiencies. By addressing these issues, businesses can create a more productive work environment.
What are qualitative factors in productivity?
Qualitative factors include things like employee morale, team dynamics, and work culture, all of which can have a significant impact on productivity even if they are not directly measurable by traditional metrics.