
According to research by Harvard Business School in 2018, 78.1% of workers involuntary experience idle time weekly, costing their employers about $100 billion a year. When employees are unproductive, it can have severe implications for business owners and their organizations. It’s good for businesses to have an idle time calculator in place to know how much time is wasted on irrelevant activities. Keep reading to learn how to calculate idle time at work!
What Is Idle Time at Work?
Idle time refers to periods when employees or machines are unproductive, regardless of whether management can influence the cause. This includes both times employees are not actively engaged, and powered-on computers remain unused.
Analyzing utilized time can reveal instances where employees are distracted by non-essential activities during work hours. A high idle percentage can signal a need to investigate potential productivity bottlenecks and explore strategies for optimizing workflow and focus. There are three different types of idle time:
- Worker’s idle time percentage: This number reflects the frequency with which employees engage in activities unrelated to work, highlighting instances of inactivity within the workplace.
- Machine idle time percentage: This metric signifies interruptions in the business process, such as equipment breakdowns or delays in supply receipts.
- Computer idle time percentage: This type of idle percentage shows when employees are not actively utilizing their computer systems during designated work hours. Also, when computers remain inactive.

Why Is It Important To Calculate Idle Time?
Minimizing idle time is vital if a company wants to avoid a drop in employee productivity and maximize its work performance over an extended period. Every second your employees or machine stay inactive accounts for lost productivity in your organization.
With the current state of remote work, it is vital to perform idle time calculation to identify the gap between your existing output productivity and peak productivity levels. No employee or machine can function at 100% efficiency, and some idle time should be expected. Yet, the goal of every business owner is to reduce idle time.
Percentage of Idle Time Formula
The percent idle time formula is very simple and is as follows:
Idle Time Percentage= (Total Time/Idle Time) × 100
Suppose an employee works for 8 hours in a day but is actively engaged in work-related tasks for only 6 hours. The idle time is the difference between the total and active time, which is 8 – 6 hours = 2 hours. Using the formula:
Idle Time Percentage= (8hours/2hours) × 100=25%
The idle time percentage is 25%, indicating that 25% of the total work hours were spent in idle or non-productive activities.
Get more out of your business
Get the best employee engagement content every week via mailing list
What Is Idle Time At Workflow
Idle time is the period of time that employees and machines are unproductive due to factors that may or may not be influenced by management. It also refers to the periods of time that powered-on computers are not being utilized. Utilized time reveals the employees who waste their active time on other trivial activities when there is a need to complete a task. A high idle time percentage indicates that workers spend more time on non-work-related tasks.
More importantly, business owners need the idle time percentages to gain insight into correcting various business processes, including cost-control, scheduling, and workflow. Furthermore, there are three different types of idle time, and they are given as follows:
Worker’s idle time percentage: refers to the number of times employees engage or do some other activities unrelated to work. It shows employee inactivity in the workplace.
Machine idle time percentage: This indicates the interruption of the business process like a breakdown of equipment, delays in the supplies receipts, and many others.
Computer idle time percentage: This type of idle percentage shows employees are not working on their computer systems during their work time. It reveals that computers remain idle when they are not being utilized. Additionally, summing up both the Idle time and desktop time equals time at work.
Note: Desktop time is the actual time spent on a system while using keyboard or mouse clicks.
Why An Employee Might Be Idle?
Insufficient Workload
When there’s an insufficient workload, employees may need more tasks to occupy their time. This situation can arise due to various factors, such as a temporary lull in projects, completion of assignments ahead of schedule, or organizational issues in task distribution.
Equipment Downtime
Employee idle time due to equipment downtime can stem from routine maintenance, unexpected malfunctions, or necessary repairs. Without the tools or machinery required for their tasks, employees are forced to wait until the issues are resolved, leading to unproductive periods.
Waiting for Dependencies
Employees may experience an idle time when their work is contingent on external factors. This could involve waiting for approvals, feedback from colleagues or clients, or essential information needed to move forward. Delays in these dependencies can result in unproductive waiting periods.
Inefficient Scheduling
Inefficient scheduling practices, such as poorly managed work hours, breaks, or shifts, can contribute to idle time. Gaps between tasks or shifts that could be more effectively utilized lead to periods where employees are not actively engaged in productive work.
Seasonal or Cyclical Fluctuations
Industries with seasonal or cyclical demand variations may witness idle periods during off-peak times. When business slows down due to external factors like holidays, economic cycles, or industry-specific trends, employees may experience reduced workloads and idle time.
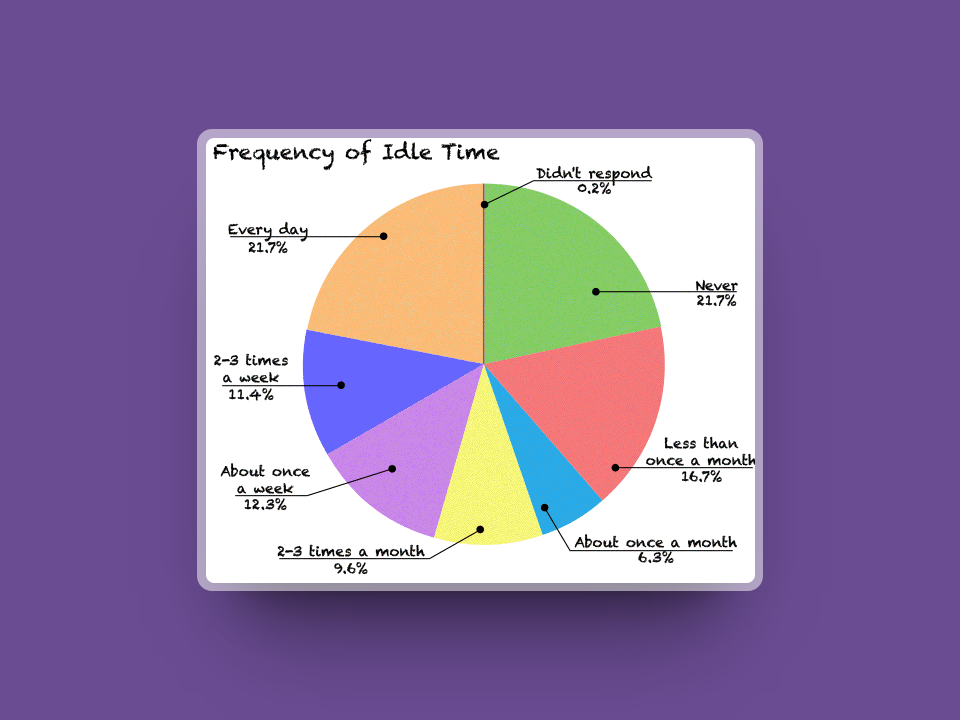
Image source: Employees were asked “On average, how frequently do you experience periods of at least 15 minutes of other-caused idle time at your primary job?” (Blair Storie-Johnson)
How to Calculate Employee Idle Time?
Do employees spending time waiting for tasks or struggling with inefficient processes drag down your team’s efficiency? Idle time, the gap between scheduled work and actual productivity can be a hidden cost mining your company’s bottom line. If you have doubts about how to find idle time, let’s help you! There are two ways to do idle time calculation:
- Manual Method: To calculate employee idle time, subtract actual work hours from standard hours. The resulting difference represents the total idle time. Actual hours indicate the total time employees are engaged in productive activities, while standard hours denote the scheduled work hours, warranting compensation.
- Time Tracking Software: Tools like Monitask use automated data entry, where employees log in and out digitally to track mouse clicks, keyboard activity, and application usage, providing a comprehensive picture of each employee’s time allocation.
Finest Time Tracking with Monitask
While many companies rely on timesheets for tracking work hours, leveraging dedicated software like Monitask enhances precision. This tool can be used to calculate idle time and foster team efficiency. Monitask offers affordable and accessible employee monitoring solutions, promoting accountability and productivity across your team. Powerful, affordable, and user-friendly, Monitask suits every business owner and manager seeking accurate records of team hours.
Wrapping Up
Employee idle time within a company can manifest in different forms, such as downtime or waiting periods, ultimately leading to a decline in revenue. Businesses ought to proactively identify the root causes of idle time among team members and take effective measures to minimize it. While there are various approaches to reducing idle time, monitoring software tools, such as Monitask, are the top choice for accurately tracking and optimizing employees’ productive hours. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the formula of idle?
Idle time formula= Total Time – Active Time. For instance, if a system runs for 10 hours but is actively used for only 7 hours, the idle time is calculated as 10 hours (total) – 7 hours (active) = 3 hours.
What is idle time with example?
Idle time is the duration a resource remains unused during its available time. For instance, if a factory machine operates for 8 hours but is only actively processing for 5 hours, the idle time is 3 hours—when the machine is present but not actively engaged in production.
How do I calculate idle time in Excel?
Idle time calculation in Excel involves subtracting active time from total time using a formula like “=Total Time – Active Time.” For example, if the total time is in cell A1 and the active time is in cell B1, use the formula “=A1-B1” in another cell to get the idle time.


